Ransomware attacks on healthcare providers pose a significant threat to patient care and data security. According to Software Advice’s 2024 Medical Cybersecurity Survey, more than 25% of ransomware attacks directly impact patient care, leading to disrupted medical services, lost data, and compromised patient safety.
This press release features multimedia. View the full release here: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20240521811121/en/
(Graphic: Business Wire)
Software Advice’s survey of cybersecurity experts in healthcare found that the vast majority (87%) of data held in today’s medical practices is digital. This vulnerability is compounded by the complexity and sheer volume of data that providers must manage and protect. Notably, 50% of healthcare organizations in the U.S. have now experienced a data breach, with 32% encountering one in the last three years.
The recent Ascension cyberattack highlights the urgent need for healthcare providers to strengthen their cybersecurity measures. The survey found that 42% of practices have experienced a ransomware attack, with 48% of these attacks impacting patient data. More than one in four (27%) of these attacks directly affect patient care.
“For most businesses, downtime resulting from a cyberattack impacts production, profits, and even reputation—but when systems go down at a healthcare facility, medical records become inaccessible, devices malfunction, and critical procedures are delayed,” said Collin Couey, medical analyst for Software Advice. “Implementing comprehensive cybersecurity measures, including response plans and employee training, is critical to mitigating these risks for patients.”
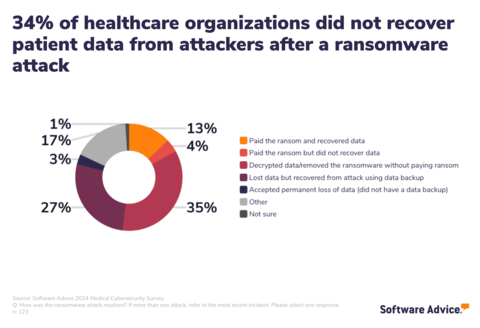
Despite the high risk, only 63% of healthcare organizations have a cybersecurity response plan in place, leaving 37% without a formalized strategy to address cyber threats. Without a formalized plan in place, healthcare providers may face significant delays in response times and increased risk of data loss. To make matters worse, over 34% of providers did not recover patient data after a ransomware attack.
Human error and targeted attacks against data security systems are the main causes of breaches. In fact, 74% of healthcare organizations spent fewer than five hours on IT security and data privacy training for their employees in 2023, with 35% dedicating two hours or fewer. With more than half (55%) of healthcare organizations allowing employees to access more data than necessary for their job roles, an increase in employee training is essential to help staff recognize and respond to cyber threats, such as pervasive phishing scams.
Couey suggests, “To help mitigate cybersecurity threats, healthcare organizations must create, maintain, and update a cybersecurity response plan that includes things such as defined roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and a prioritization list.”
Read the full report on Software Advice to learn more about medical cybersecurity threats and tips to prevent and mitigate attacks. Healthcare providers can also explore cybersecurity software options to bolster their defenses.
About Software Advice
Software Advice simplifies software buying. Through 1-on-1 help and trusted insights, industry savvy real-life advisors guide buyers to top software options in minutes instead of days. Software Advice has delivered over 1 million software recommendations to help businesses find the right fit for their industry, since its launch in 2005. Software Advice also features over 2 million verified user reviews to help people feel confident in their technology decisions.
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20240521811121/en/