MarinHealth announced today that it performed its first vascular surgical procedure for aneurysm repair utilizing advanced AI technology. Allan Conway, MD, Clinical Associate Professor of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, UCSF and MarinHealth, and the vascular surgical team applied Cydar Maps augmented artificial intelligence technology, making the MarinHealth vascular surgical team one of few teams nationwide capable of using this advanced system.
This press release features multimedia. View the full release here: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20240724398683/en/
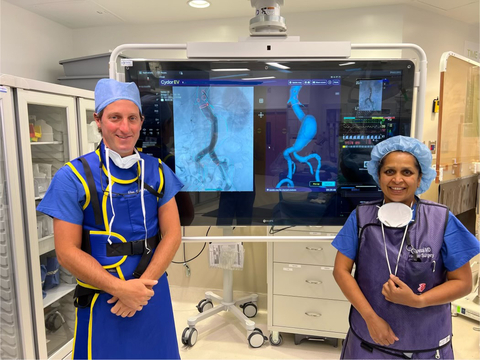
Pictured are Allan Conway, MD, Clinical Associate Professor of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, UCSF and MarinHealth, and Tina Desai, MD, Vascular Surgery, MarinHealth. (Photo: Business Wire)
The AI-equipped Cydar Maps surgical platform enables surgeons and clinicians to create a detailed 3D map personalized to each patient’s unique anatomy for pre-surgical planning, real-time image guidance during surgery, and automated post-operative evaluation of surgical outcomes. Cydar Maps not only enhances the surgeon’s visualization but also aids the surgeon’s decision-making in the operating room and helps guide decisions throughout the entire patient care pathway, resulting in better patient outcomes and improved efficiency.
“Integrating Cydar Maps is part of MarinHealth’s ongoing commitment to stay at the forefront of innovative solutions and treatments, providing our community with access to the best treatment options available,” commented David Klein, MD, CEO of MarinHealth.
“This cutting-edge technology empowers surgeons to navigate complex vascular procedures with greater precision. Plus, it provides advanced tools that enable physicians to track aneurysm volume over time,” said Conway. “This is a significant milestone as we aim to revolutionize endovascular aortic treatment with cutting-edge, digital solutions. It empowers surgeons with more knowledge, which ultimately improves patient outcomes.”
The MarinHealth Vascular Surgery team treats patients in four locations throughout Northern California, including Greenbrae, Novato, Santa Rosa, and Sonoma. To learn more about this innovative AI-based solution, go to https://cydarmedical.com/cydar-maps/.
The adoption of Cydar Maps technology at MarinHealth Medical Center was made possible through the generous support of donors of the MarinHealth Foundation.
About MarinHealth
MarinHealth is an integrated healthcare enterprise with deep roots in the North Bay. With a world-class physician and clinical team, an ever-expanding network of clinics, and a new state-of-the-art hospital, MarinHealth stops at nothing to help patients achieve their best health. MarinHealth is comprised of MarinHealth Medical Center, a 327-bed hospital located in the heart of Marin since 1952, the MarinHealth Medical Network with 55+ primary care and specialty clinics located in Marin, Sonoma, and Napa counties, and the MarinHealth Foundation. A long-time partnership with UCSF expands MarinHealth’s world-class capabilities and its portfolio of services to serve more of our North Bay community in new and better ways. For more information, visit MyMarinHealth.org.
About Cydar Medical
Cydar Medical, based in Cambridge, United Kingdom, offers a comprehensive suite of tools designed to enhance minimally invasive image-guided endovascular surgeries. Our flagship product, Cydar Maps, supports pre-surgical planning, real-time image guidance during surgery, and automated post-operative evaluation of surgical outcomes. Leveraging the power of AI, Cydar enhances surgical visualization and decision-making not only in the operating room but throughout the entire patient pathway.
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20240724398683/en/